How to Apply for Dental Implants Through the HSE
Applying for dental implants through the HSE involves following a defined referral and assessment process and meeting specific clinical requirements. This guide explains the typical steps in making an application, starting with an initial consultation in primary dental care and progressing to specialist evaluation where appropriate. It outlines the dental and medical factors that are usually reviewed, what supporting information may be requested, and how decisions about HSE funding are made. The guide also covers expected waiting times and what applicants can do to prepare for assessments. Where treatment is not approved within the public system, alternative options are outlined to help individuals plan their next steps with clarity.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
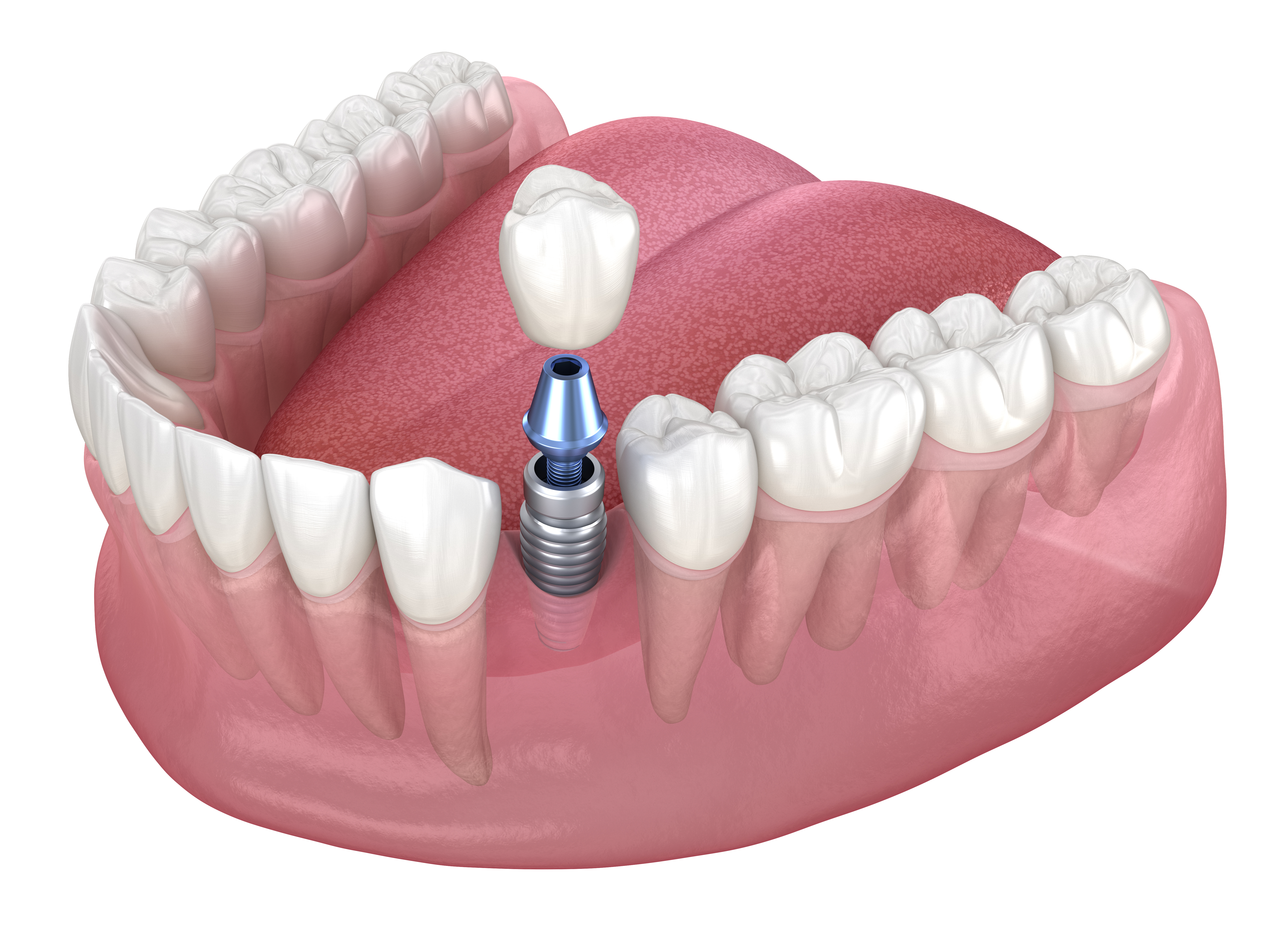
Dental implants represent a significant advancement in restorative dentistry, offering a durable solution for missing teeth. In Ireland, the Health Service Executive (HSE) provides a pathway for eligible individuals to access dental implant treatment. This process is highly structured, focusing on specific clinical needs and criteria to ensure that public health resources are directed effectively. Understanding the various stages and requirements is essential for anyone considering applying for this treatment through the HSE.
What Clinical Requirements Must Be Met for HSE Dental Implants?
Eligibility for dental implants through the HSE is primarily determined by clinical necessity rather than cosmetic preference. Applicants must typically present with significant functional impairment due to tooth loss, which cannot be adequately addressed by conventional prosthetic solutions like dentures or bridges. Common scenarios include individuals who have lost multiple teeth, experienced trauma, or have congenital conditions leading to tooth absence. The assessment will also consider the overall oral health, bone density, and the presence of any active periodontal disease, which must be managed before implant placement can be considered. A stable and healthy oral environment is a prerequisite for successful implant integration and long-term prognosis.
The HSE Application Pathway: From Primary Dental Care to Specialist Assessment
The journey for HSE dental implants generally begins with a referral from a primary care dentist. Your local dentist will assess your oral health, discuss your needs, and determine if a referral to a specialist within the HSE system is appropriate. This initial assessment will involve a thorough examination, possibly including X-rays and other diagnostic imaging. If your case meets the initial criteria for specialist consideration, your dentist will then refer you to a HSE-funded consultant oral and maxillofacial surgeon or a consultant in restorative dentistry. This specialist will conduct a more in-depth evaluation to confirm eligibility and plan the potential course of treatment.
Medical and Dental Factors Reviewed During the HSE Evaluation Process
During the specialist assessment, a comprehensive review of both your medical and dental history will be undertaken. Medical factors such as systemic health conditions (e.g., uncontrolled diabetes, severe cardiovascular disease), certain medications (e.g., bisphosphonates), and smoking habits can influence the success rate of dental implants and may be contraindications. Dental factors include the quality and quantity of available bone, the condition of adjacent teeth, occlusal forces, and the overall prosthetic space. The specialist panel will weigh these factors carefully to determine the suitability for implants and the likelihood of a successful outcome within the HSE framework. The decision-making process prioritizes cases where implants offer the most significant functional improvement and where the patient’s health status supports the procedure.
Supporting Documentation, Decision-Making, and Expected Waiting Times
Applicants will need to provide comprehensive supporting documentation, typically submitted by the referring dentist. This includes detailed clinical notes, radiographs, study models, and any relevant medical reports. The decision-making process is handled by a specialist panel within the HSE, who review each case against established clinical guidelines. Due to high demand and resource limitations, there can be significant waiting times for both specialist assessment and the actual implant procedure. These waiting times can vary depending on the complexity of the case and the specific HSE region. It is important for applicants to maintain regular communication with their referring dentist and the HSE to stay informed about the status of their application.
What Options Are Available if HSE Dental Implants Are Not Approved?
If an application for dental implants through the HSE is not approved, or if the waiting times are not feasible for the patient, several alternative options are available. These typically involve private dental care. Patients can explore private clinics that offer dental implants, often with a wider range of treatment choices and potentially shorter waiting periods. Additionally, conventional solutions like dentures (full or partial) or fixed dental bridges remain viable alternatives for replacing missing teeth. While these options may not offer the same benefits as implants in terms of bone preservation or stability, they can still restore function and aesthetics. It is advisable to discuss these alternatives thoroughly with a dental professional to determine the most suitable path based on individual needs and financial considerations.
| Service/Option | Description | Estimated Cost Range (EUR) |
|---|---|---|
| HSE Approved Implants | Covered by public health system for eligible cases | No direct cost (covered by HSE) |
| Private Single Dental Implant | Surgical placement of one implant and crown | €2,000 - €4,000 |
| Private Multiple Dental Implants | Cost per implant decreases with multiple units | €1,800 - €3,500 per implant |
| Full Arch Implants (e.g., All-on-4) | Replacing a full arch of teeth with 4-6 implants | €10,000 - €25,000 per arch |
| Conventional Dentures (Full) | Removable prosthesis for all missing teeth | €500 - €1,500 |
| Conventional Bridge (Per Unit) | Fixed prosthetic replacing one or more teeth | €600 - €1,200 per unit |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Navigating the HSE system for dental implants requires patience and a clear understanding of the clinical and administrative processes involved. While the HSE aims to provide this advanced treatment to those with the most critical clinical need, private options and conventional alternatives remain accessible for individuals who do not meet the public health criteria or prefer a different pathway. Consulting with a dental professional is the most effective way to understand all available options and make an informed decision regarding dental implant treatment in Ireland.