The Intriguing World of Octopuses: Cephalopod Intelligence and Behavior
Octopuses, the most intelligent of all invertebrates, have long fascinated scientists and marine enthusiasts alike with their enigmatic behavior and remarkable learning capabilities. This article delves into the captivating world of octopuses, shedding light on their behavior, intelligence, and the latest research surrounding these extraordinary creatures.
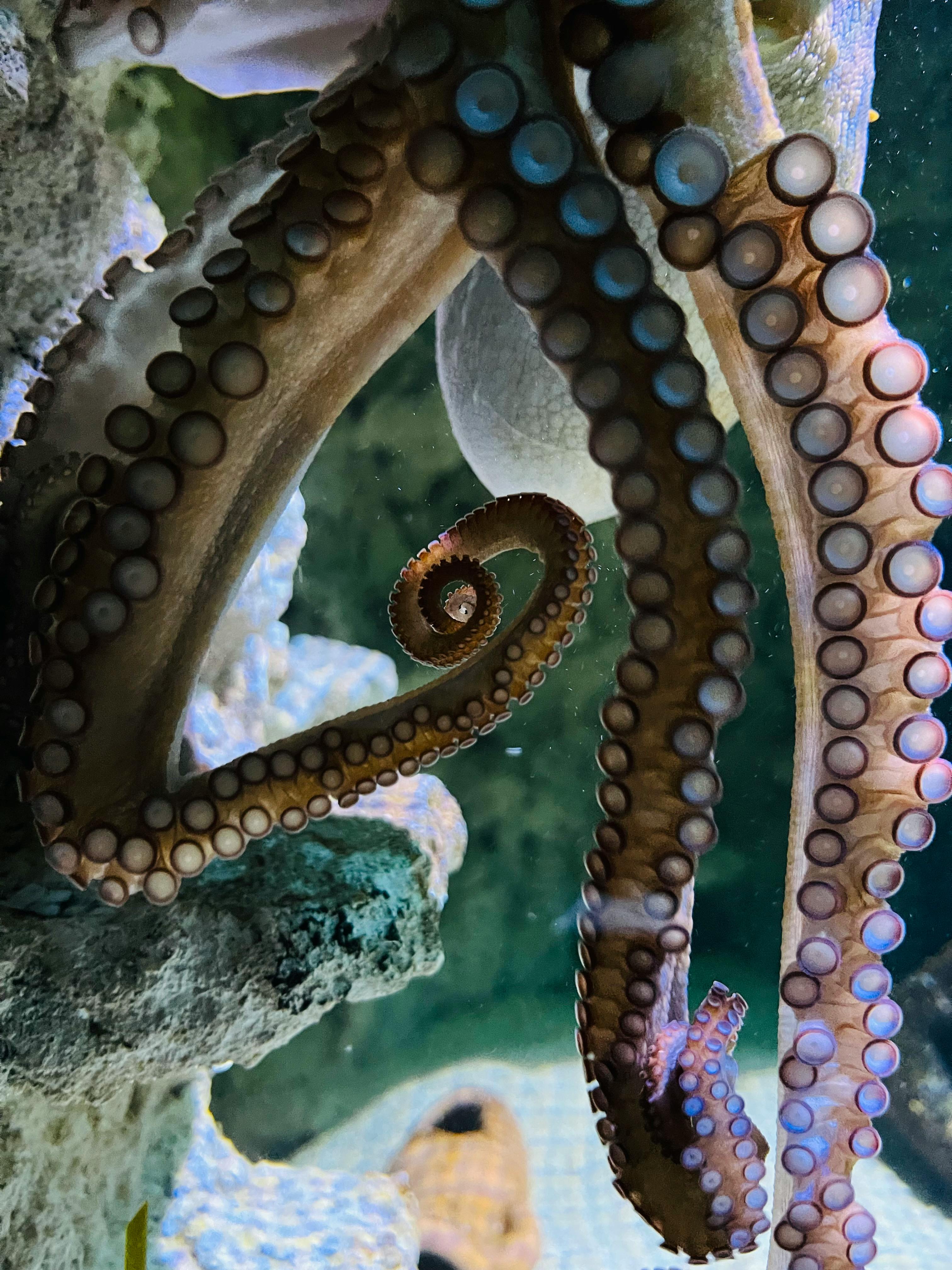

A Glimpse into the Octopus’s World
The octopus’s world is an intriguing one. These incredibly adaptable creatures are found in every ocean on the planet, from the warm waters of the tropics to the freezing depths of the Antarctic. They belong to the family of cephalopods, which also includes squids and cuttlefish. Octopuses are known for their eight arms, bulbous heads, and three hearts that pump blue, copper-rich blood.
Historically, octopuses have been a subject of fascination and mystery. Ancient seafarers spun tales about monstrous sea creatures, many of which were likely based on encounters with large octopuses. Today, scientific research continues to uncover new aspects about the biology and behavior of these remarkable creatures.
The Intelligence of Octopuses
Octopuses are renowned for their intelligence. They have the largest brains of any invertebrate, and their cognitive abilities rival those of many vertebrates. Laboratory tests have shown that octopuses can solve complex puzzles, open child-proof jars, and even recognize individual humans.
Recent studies have provided fascinating insights into the mechanisms behind their cognitive abilities. Unlike humans and other vertebrates, whose intelligence is centralized in the brain, octopuses have a distributed nervous system. Two-thirds of their neurons are found in their arms, which can independently taste, touch, and control movement.
Behavioral Aspects
Octopuses exhibit a range of interesting behaviors. They are known for their camouflage abilities—changing color and texture to blend in with their surroundings. This skill is used not only to evade predators but also to communicate and express emotions.
More recently, researchers have documented instances of octopuses engaging in what appears to be play behavior—another sign of their advanced cognitive abilities. For example, captive octopuses have been observed arranging and rearranging objects in their tanks, seemingly for their own amusement.
The Role of Octopuses in Marine Ecosystems
Beyond their fascinating biology and behavior, octopuses also play a crucial role in marine ecosystems. They are both predators and prey, helping to maintain the balance of species in their habitats. Furthermore, their burrowing habits contribute to the physical structure of the seafloor, providing homes for a variety of other marine creatures.
The Future of Octopus Research
The study of octopuses is a rapidly evolving field. Researchers are keen to further explore the extent of their cognitive abilities and their complex behaviors. Current studies are also looking at their genome in an attempt to understand the genetic basis for their intelligence and unique characteristics.
In conclusion, octopuses represent one of the most fascinating areas of animal research. They challenge our understanding of intelligence and behavior, offering a captivating glimpse into an alien world. As we continue to delve into the secrets of these remarkable creatures, it’s clear that we have much more to learn and discover about the intriguing world of octopuses.